TROPION-Breast04 Study
Therapy with antibody-drug conjugate and immunotherapy or standard therapy in previously untreated patients with early-stage triple-negative breast cancer
Recruitment for the TROPION-Breast04 study has already been completed.
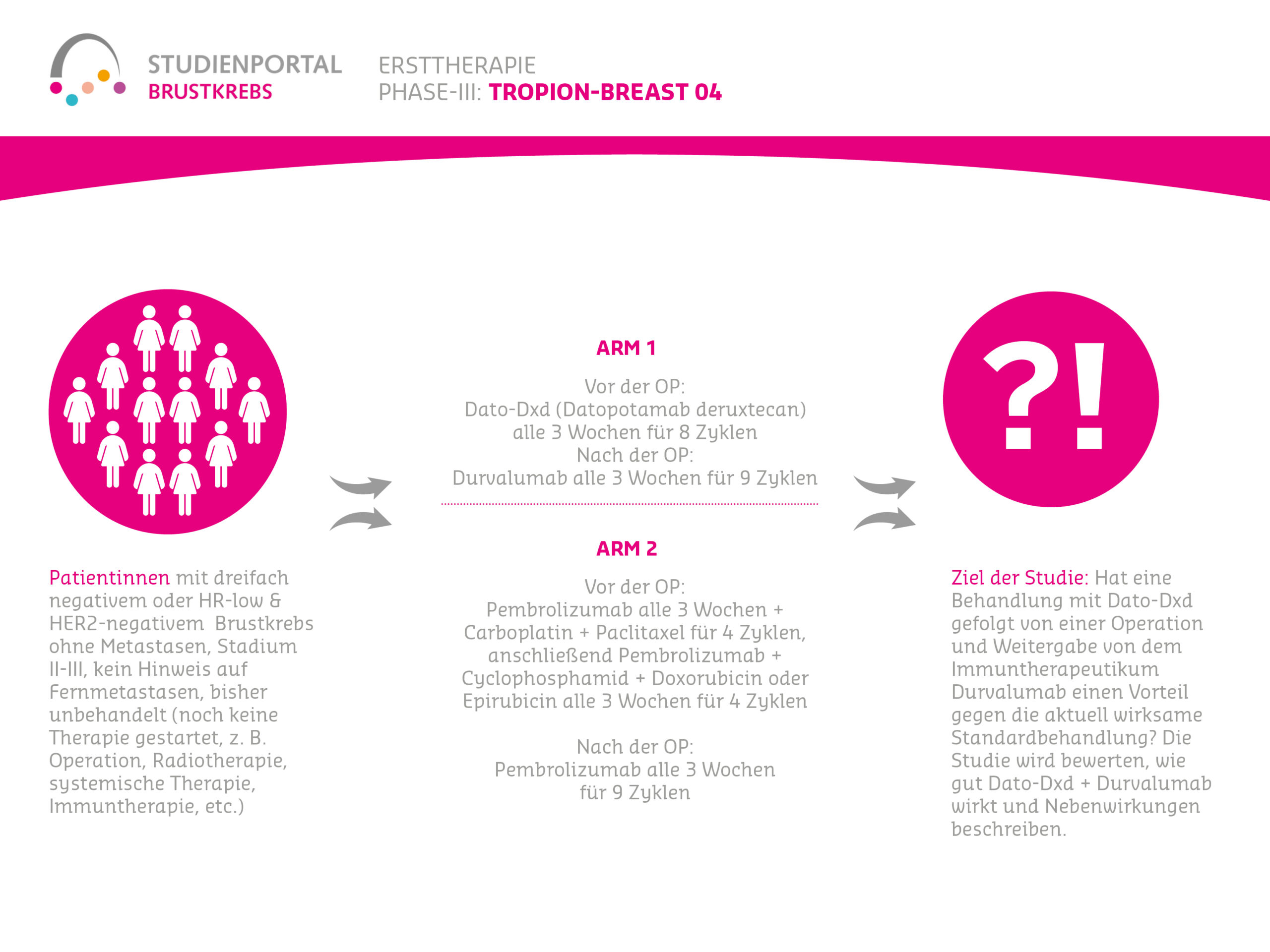
TROPION-Breast04 is a randomized (treatment assignment for the specific patient is by chance), controlled, Phase 3 therapy study. The study compares a new therapy against the current standard treatment and is aimed at patients with triple-negative (or hormone receptor-low, “HR-low”/ HER2-negative), early (Stage II or III) breast cancer. Furthermore, these patients have not yet received any treatment (treatment-naive).
What is being investigated in this study?
Datopotamab deruxtecan (Dato-DXd) is a drug consisting of two parts: Datopotamab (an antibody) and deruxtecan (a cancer drug), which are linked together. Datopotamab binds to a protein called Trophoblast Cell Surface Antigen 2 (TROP2), which is found on TNBC tumors. TNBC stands for “triple negative breast cancer”. This means that the breast cancer cells do not have receptors (protein compounds on the cell nucleus or cell membrane) for estrogen, progesterone, and HER2. Once bound, Dato-DXd is taken up into the tumor cell, where Deruxtecan is released to kill the tumor. Durvalumab is a drug that blocks the activity of a protein called PD-L1, making tumors more susceptible to being killed by the body’s own immune cells.
In previous studies with patients with TNBC who were treated with Dato-DXd alone (TROPION-PanTumor01) or in combination with Durvalumab (BEGONIA study), efficacy against breast cancer was observed.
What is the aim of the study?
The study targets patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), a type of breast cancer where the cells lack HER2, estrogen, or progesterone receptors. The current standard treatment for patients with TNBC is initial treatment with Pembrolizumab, combined with chemotherapy, followed by the removal of the tumor and lymph nodes from the armpit. Pembrolizumab is continued for a total of one year after surgery. Despite this highly effective tumor treatment, not all patients are cured. Therefore, this treatment needs to be improved so that more patients with TNBC can be cured.
Therefore, the TROPION-Breast04 study will investigate whether Dato-DXd combined with Durvalumab, followed by surgery and continued Durvalumab, is more effective than the current standard treatment for these patients. The study will evaluate how well Dato-DXd plus Durvalumab works and describe the side effects.
How is the study conducted?
Within the study, there are two treatment arms (treatment options) to which patients are randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio:
Arm 1:
Before surgery (neoadjuvant):
Datopotamab deruxtecan together with Durvalumab as an intravenous infusion every 3 weeks for 8 cycles (infusions)
After surgery (adjuvant):
Durvalumab as an intravenous injection every 3 weeks for 9 cycles
Arm 2:
Before surgery (neoadjuvant):
Pembrolizumab as an intravenous infusion every 3 weeks together with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel for 4 cycles. Subsequently, Pembrolizumab and Cyclophosphamide and Doxorubicin or Epirubicin as an intravenous infusion every 3 weeks for 4 cycles
After surgery (adjuvant):
Pembrolizumab as an intravenous infusion every 3 weeks for 9 cycles
Are there risks?
You will be informed about possible risks or side effects associated with participation during an informational discussion.
Eligibility Criteria
Men and women aged 18 years and older can participate in this study, with:
- Triple-negative or HR-low & HER2-negative breast cancer without metastases
- Stage II-III
- No evidence of distant metastases
- Previously untreated (no therapy started yet, e.g., surgery, radiotherapy, systemic therapy, immunotherapy, etc.)
In addition, there are further criteria that must be met for participation in the study. Interested patients should speak with the investigators at a study center, who can check if this study is suitable for them.
Where can I participate in this study?
Further information on participating centers can be found here:
https://studienportal-brustkrebs.de/deutschlandkarte
This study is supported by: